Regular exercise is not only beneficial for overall health and well-being but also plays a crucial role in managing chronic diseases. In this article, we will explore the significant impact of exercise on various chronic health conditions, highlighting the positive outcomes it brings to individuals’ lives. From cardiovascular health and diabetes management to mental well-being and cancer prevention, effects of exercise on chronic diseases.
By understanding these effects, individuals can embrace physical activity as a powerful tool in their journey towards improved health and enhanced quality of life. Now, we explore how does exercise reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
1. Cardiovascular Health

Exercise plays a critical role in preventing and managing heart disease by positively impacting cardiovascular health. Here are key points highlighting impact of exercise on cardiovascular health and its role in preventing and managing heart disease:
1. Strengthens the Heart: Regular exercise strengthens the heart muscle, improving its efficiency and pumping ability.
2. Reduces Blood Pressure: Physical activity helps lower blood pressure, reducing the strain on the heart and decreasing the risk of hypertension.
3. Improves Cholesterol Levels: Exercise increases HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol) while decreasing LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol), promoting a healthier lipid profile and reducing the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries.
4. Enhances Circulation: Exercise improves blood flow and circulation, ensuring that oxygen and nutrients reach the body’s tissues more efficiently.
5. Promotes Cardiovascular Fitness: Engaging in aerobic exercises like brisk walking, running, cycling, or swimming improves cardiovascular fitness, increasing endurance and stamina.
6. Reduces Inflammation: Exercise has anti-inflammatory effects, reducing inflammation in blood vessels and decreasing the risk of atherosclerosis.
7. Lowers Stress and Anxiety: Regular exercise is known to reduce stress and anxiety levels, which can contribute to better heart health.
8. Improves Heart Function: Exercise can improve heart function and overall cardiac health, enhancing the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
By incorporating regular exercise into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and manage existing heart conditions more effectively. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to develop a safe and personalized exercise plan based on individual needs and abilities.
2. Diabetes Management

The another effects of exercise on chronic diseases like diabetes, particularly in terms of blood sugar control and overall disease management. Here are key points highlighting the impact of exercise on diabetes management:
1. Blood Sugar Control: Engaging in regular physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity, allowing glucose to be utilized more effectively by the body’s cells.
2. Improved Insulin Function: Exercise enhances insulin function, helping the body to better regulate blood sugar levels and reducing the reliance on diabetes medications.
3. Weight Management: Exercise plays a crucial role in weight management, as excess weight can contribute to insulin resistance. Regular physical activity aids in weight loss or maintenance, improving insulin sensitivity.
4. Cardiovascular Health: Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Exercise improves cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and cholesterol abnormalities.
5. Enhanced Overall Fitness: Engaging in aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, or swimming improves cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and endurance, contributing to better overall health for individuals with diabetes.
6. Stress Reduction: Exercise helps reduce stress levels, which can have a positive impact on blood sugar control and overall well-being.
3. Weight Management

Exercise plays a significant role in managing chronic health diseases, particularly in terms of weight management. Here are key points highlighting the impact of exercise on weight management:
1. Calorie Expenditure: Engaging in regular physical activity helps burn calories, contributing to weight loss or maintenance.
2. Increased Metabolic Rate: Exercise boosts metabolism, which helps the body burn more calories even at rest, aiding in weight management.
3. Muscle Development: Resistance training exercises promote muscle growth, which increases muscle mass. Since muscles burn more calories than fat, having more muscle can contribute to weight loss and weight maintenance.
4. Appetite Regulation: Exercise can help regulate appetite and reduce cravings, making it easier to manage calorie intake and control weight.
5. Improved Body Composition: Regular exercise, especially a combination of cardiovascular and strength training exercises, can lead to a decrease in body fat percentage and an increase in lean muscle mass, resulting in a healthier body composition.
6. Enhanced Energy Expenditure: Physical activity increases energy expenditure, allowing for a larger calorie deficit, which is essential for weight loss.
7. Long-Term Weight Maintenance: Exercise is crucial for sustaining weight loss and preventing weight regain. Regular physical activity helps individuals maintain their weight loss results and stay at a healthy weight.
4. Mental Health

Exercise has a profound impact on mental health and plays a significant role in managing chronic health diseases. Here are key points highlighting the impact of exercise on mental health:
1. Mood Enhancement: Regular physical activity stimulates the release of endorphins, known as “feel-good” hormones, which can help alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress.
2. Stress Reduction: Exercise serves as a healthy outlet for stress and tension, promoting relaxation and reducing the negative effects of chronic stress on mental well-being.
3. Improved Sleep Quality: Engaging in regular exercise can enhance sleep quality and duration, reducing the risk of sleep disorders and promoting better mental and emotional well-being.
4. Boosted Self-esteem: Regular exercise can enhance self-esteem and body image, leading to improved self-confidence and a positive outlook on life.
5. Cognitive Function: Exercise has been shown to improve cognitive function, including memory, attention, and decision-making skills, which can positively impact overall mental health.
6. Social Interaction: Participating in group exercise classes or team sports provides opportunities for social interaction and support, which can help combat feelings of isolation and improve mental well-being.
5. Bone Health
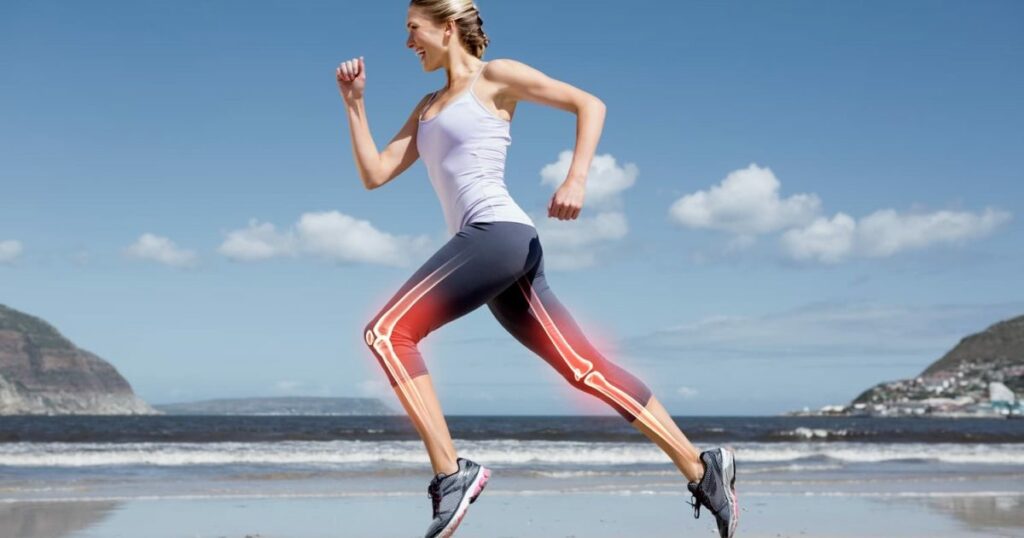

Exercise has a positive impact on bone health, making it essential for managing chronic health diseases. Here are key points highlighting the impact of exercise on bone health:
1. Increased Bone Density: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, and strength training, stimulate bone growth, increase bone density, and help prevent conditions like osteoporosis.
2. Improved Bone Strength: Exercise strengthens the muscles surrounding the bones, providing better support and reducing the risk of fractures and injuries.
3. Enhanced Balance and Stability: Certain exercises, including yoga and tai chi, can improve balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and fractures, especially in individuals with conditions like osteoporosis.
4. Ongoing Bone Development: Regular weight-bearing exercises during childhood and adolescence promote optimal bone development, leading to stronger bones throughout life.
5. Healthy Joint Function: Exercise helps maintain joint flexibility, reducing the risk of joint-related chronic diseases like osteoarthritis.
6. Respiratory Conditions
Exercise has a significant impact on managing chronic respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Here are key points highlighting the impact of exercise on respiratory health:
1. Improved Lung Function: Engaging in regular aerobic exercises, like walking, swimming, or cycling, helps strengthen respiratory muscles and enhances lung capacity, leading to improved breathing and oxygen uptake.
2. Reduced Breathlessness: Exercise training can help individuals with respiratory conditions better tolerate physical exertion and reduce the sensation of breathlessness during daily activities.
3. Enhanced Mucus Clearance: Physical activity promotes the clearance of mucus from the airways, reducing the risk of infections and exacerbations in individuals with respiratory conditions.
4. Weight Management: Regular exercise aids in weight management, reducing the strain on the respiratory system and improving overall lung function.
5. Enhanced Quality of Life: Engaging in physical activity can improve overall fitness, boost energy levels, and enhance the quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions.
7. Chronic Pain Management
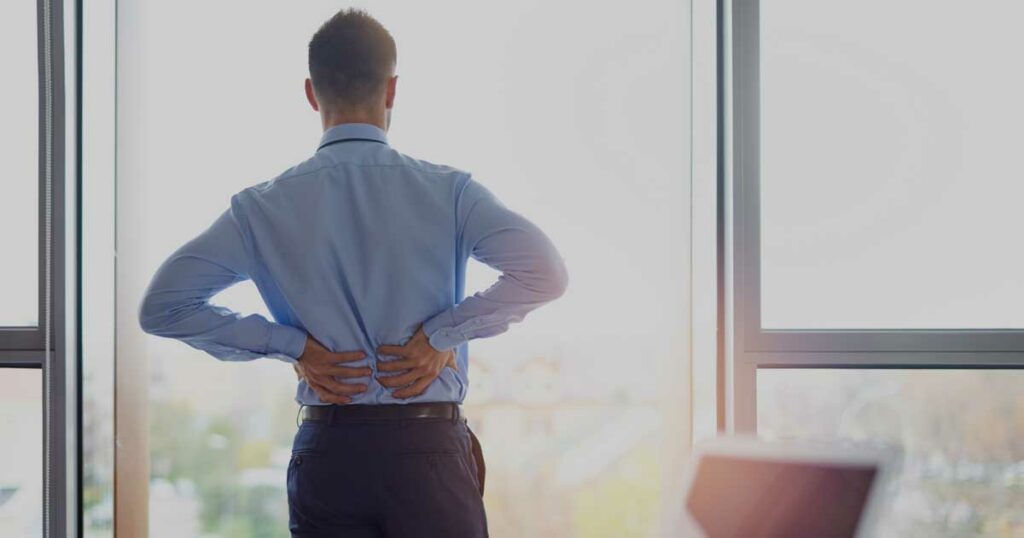

Regular Exercise impact on chronic pain associated with various health conditions. Here are key points highlighting the impact of exercise on chronic pain management:
1. Pain Reduction: Engaging in regular exercise can help alleviate chronic pain by releasing endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers.
2. Improved Strength and Flexibility: Exercise helps strengthen muscles and improve flexibility, which can reduce pain and improve overall functionality.
3. Enhanced Joint Function: Specific exercises can help alleviate joint pain by improving joint stability, reducing inflammation, and increasing range of motion.
4. Improved Mood: Exercise promotes the release of “feel-good” neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which can positively impact mood and help individuals better cope with chronic pain.
5. Better Sleep: Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, which is crucial for pain management and overall well-being.
Conclusion
These are the positive effects of exercise on chronic diseases. From cardiovascular health and diabetes management to mental well-being and chronic pain management, regular physical activity offers a multitude of benefits.
Related: 15 Healthy habits for everyday lifestyle.
By incorporating exercise into their lifestyle, individuals can take control of their health, improve their quality of life, and effectively manage chronic conditions. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals and design personalized exercise programs to ensure safety and maximize the benefits derived from physical activity for managing chronic health diseases. Embrace the power of exercise and witness its transformative effects of exercise on chronic diseases.


